Scaling Up Battery Production with 425+ New Factories
Introducing the world’s first comprehensive battery factory database covering the OEM's scaling up battery production capacity with new factories and industry trends in battery chemistry.
Exponential Industry and Ratel Consulting bring you the world’s first comprehensive database and map of battery cell and pack manufacturing gigafactories.
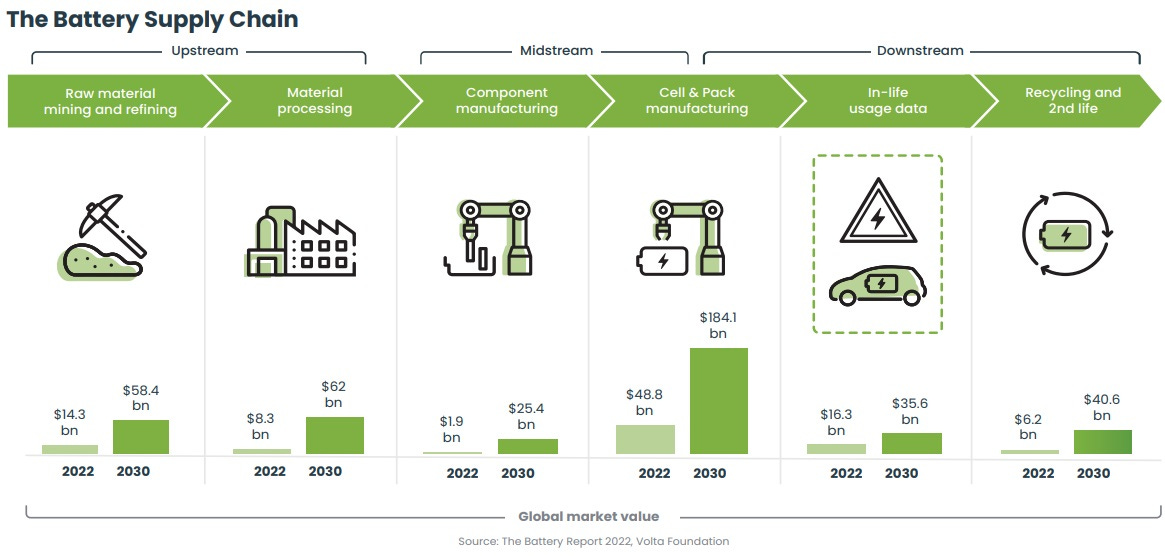
The battery supply chain is a complex and interconnected network of companies and organizations involved in producing, distributing, and recycling batteries. The supply chain can be divided into six main segments:
Raw material mining and refining: This segment involves extracting raw materials from the earth, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Material processing: This segment involves the processing of raw materials into battery-grade materials for use in anodes, cathodes, and electrolytes.
Component manufacturing: This segment involves the manufacturing of battery components, such as separator films, current collectors, and battery housings.
Cell & pack manufacturing: This segment involves the assembly of battery cells and battery packs.
In-life usage data: This segment involves collecting and analyzing battery performance and usage data.
Recycling and second life: This segment involves the recycling of spent batteries and the repurposing of battery components for second-life applications.
According to the Volta Foundation, the market value of the battery supply chain is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles and other battery-powered devices. By 2030, the cell & pack manufacturing segment is expected to explode in value to $184 billion retaining its importance of roughly half the total value of the supply chain ecosystem.
The growth of the battery supply chain is creating new opportunities for businesses and investors. To help stakeholders navigate the rapid development in battery technology, manufacturing, and supply chain, Ratel Consulting and Exponential Industry are providing a comprehensive validated database, map, and analytics of over 425 announced and operational battery cell and pack gigafactories.
Mapping the Battery Cell & Pack Gigafactories
The database includes the battery’s original equipment manufacturer (OEM), factory location, factory status, capacity, capacity scheduling, battery chemistry, cell format, and more while the map brings it all to life for you to explore!
For those new to Felt, check out the help center. You can toggle layers and individual point series on and off by clicking the “👁️” icon.
Factory Status
Much of the world’s announced capacity for battery packs has yet to come online. This is because the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is still growing, and the supply of battery packs is not yet keeping pace. As a result, many battery manufacturers are investing in new plants to increase production capacity.
By our count, currently, there are only ~25 battery pack manufacturing plants in operation around the world. Flash forward to 2030 and this number is expected to grow to over 500. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for EVs, as the battery pack is the most expensive component of an EV, as well as the development of new battery technologies.
Battery OEM
Battery pack original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) that are able to scale up capacity early on have the opportunity to become dominant in the emerging electric vehicle (EV) industry. This is because the first companies to scale up can take advantage of economies of scale: as production increases, the cost of each battery pack decreases. This makes it possible for companies to offer lower prices, which can give them a competitive advantage. CATL currently commands around a third of annual global capacity with BYD, Panasonic, and LG Energy Solutions racing to catch up.
There are also challenges associated with being the first to scale up. Battery OEMs need to have a strong financial position and be able to manage the risks associated with rapid growth. But, recent government incentives (more on that below) should reduce the risk of battery OEMs failing prematurely due to not having enough cash.
Battery Chemistry
Among the scaling-up risks is developing the most performant battery, which may require placing bets on a subset of battery chemistries. This is because different battery chemistries have different performance characteristics, material costs, and manufacturing steps. If the OEMs choose the wrong chemistry, they could face significant challenges with industry oversupply, lack of long-term demand, or being too costly to scale up.

It is also important to view the overall scale and capacity in the context of battery chemistry. For example, a lithium-ion battery factory with a capacity of 50 GWh is a significant undertaking, even though 50+ are currently planned. However, building a solid-state battery factory with the same capacity would be even more challenging. Since solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of development, the manufacturing process is not yet well-established introducing a huge technology risk into an already challenging production ramp. In the end, solid-state battery technology may be preferred by automotive OEMs due to lower risk of fire (i.e. thermal runaway) and increased energy density.
Government Incentives are Driving the Growth of the Battery Manufacturing Industry
The boom in battery manufacturing is a major development that has the potential to transform the global energy landscape. Government stimulus is playing a key role in accelerating this boom, and it is likely that we will see even more growth in battery manufacturing in the years to come. As the Green Finance Institute puts it,
Governments globally continue to commit to electrifying transport and meeting net zero targets, stimulating EV uptake and demand for automotive batteries. Extensive policy support in major markets to attract some of the supply chain speaks to the strategic importance of the sector and its role in energy security; the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the US, and the EU Green Deal have both already stimulated huge amounts of private investment. Though the UK already offers extensive support for the automotive sector, it is yet to respond with a similar broader strategy.
Exponential Industry covers battery manufacturing and other strategic sectors in our weekly digest and posts. We’ve recently dove into the details of the key government programs reducing enabling OEMs to acquire financing and scale up the domestic capacity of strategic goods in energy, semiconductor, and transportation:
What’s Next With the Future of the Battery Supply Chain
Exponential Industry and Ratel Consulting will keep you posted on future developments in the battery supply chain. Let us know in the poll and comments below what you would like to see next!
Analytics and dashboard on top of the battery cell and pack database. Providing insight into capacity forecasted to come online by region and format.
Adding material processing factories and mineral deposit locations from the other segments of the battery supply chain to the database and map.
Updates to the cell and pack database and map. Including updates and revisions to the previously announced plans by the battery OEMs.
NOTE: Ratel Consulting LLC provides the Global Battery Factory Database “as is” and makes no guarantee that any of it is accurate or complete. User shall bear full responsibility and risk as to the accuracy, completeness, usefulness, performance, and results derived from any analysis performed using the Global Battery Factory Database.