Physical AI Secrets (Spoiler: It's Already Here)
This week: Patent or trade secret (paid), CAM software, additive glocal mass customization, robot chemistry, real-time VLAs, evolutionary binary thermo-mechanics, MCP, AI machinery
Shop Talk
Capturing this week's zeitgeist
Manufacturing and technology permeate every aspect of our daily lives, from the smartphone in your pocket to the infrastructure beneath our feet; yet, we rarely pause to consider the revolutionary moments that gave birth to these now-ubiquitous innovations. During a recent visit to San Francisco for the Data and AI Summit, I was struck by the city's role as the stage for aviation's grand debut at the 1915 Panama-Pacific International Exposition, where crowds gathered in wonder to witness flying machines that seemed to defy the very laws of nature. What captivated thousands as a miraculous spectacle has become so routine that we board planes with barely a thought for the engineering marvel carrying us through the sky. It makes me wonder: will our children's children look back at 2025 as the pivotal moment when Physical AI, robots seamlessly integrated into manufacturing, logistics, and daily life, transitioned from experimental curiosity to invisible backbone of civilization? Just as we forget to marvel at flight, future generations may take for granted and even forget how to make the intelligent machines that will reshape how we make, move, and manage everything around us.
Assembly Line
This week's most influential Industry 4.0 media.
The Hidden Company Powering Your CAM Software (Fusion, Mastercam & More)
ModuleWorks technology powers the toolpaths within popular CAM software, including Fusion 360, Mastercam, Siemens NX, and others. If you’ve ever run a CNC machine, you’ve likely relied on their work, whether you knew it or not.
Toolpath Closes Strategic Investment Round, Led by Kennametal, to Revolutionize CNC Machining and Manufacturing Using AI /Toolpath/
🖨️ Additive Manufacturing is No Longer the Future
By mid-2025, additive manufacturing (AM) has broken out of the prototyping corner and taken center stage as a pillar of Industry 4.0. With a global market value projected to soar from $20.37 billion in 2023 to $88.28 billion by 2030, at a staggering 23.3% CAGR, AM is no longer an emerging technology—it is a strategic enabler of design freedom, supply chain resilience, and sustainable production.
2025 IP landscape is shifting. With digital inventories and mass customization, we’re entering an era of design ownership complexity. Licensing platforms and blockchain verification may offer the next frontier in securing AM intellectual property.
Read more at Addithive
How U.S. Manufacturers Are Using 3D Printing to Bypass Tariffs, Build Resilience /DaDT/
Our New UV Curing System Enhances Additive Manufacturing /Magnoric/
Detecting 3D-Printing Defects in Real Time /Department of Energy Office of Science/
🦾🧪 Dunia's Robot-Lab That Could Win the Next Nobel Prize
New Iridium Raises $2.65M in Seed Funding to Accelerate Sustainable Chemical Platform /GlobeNewswire/
Why Bayesian Optimization Can Fall Short for Materials Innovation /Citrine/
A Niche Plastics Ingredient, Ethane, Becomes a Trade War Bargaining Chip /Bloomberg/
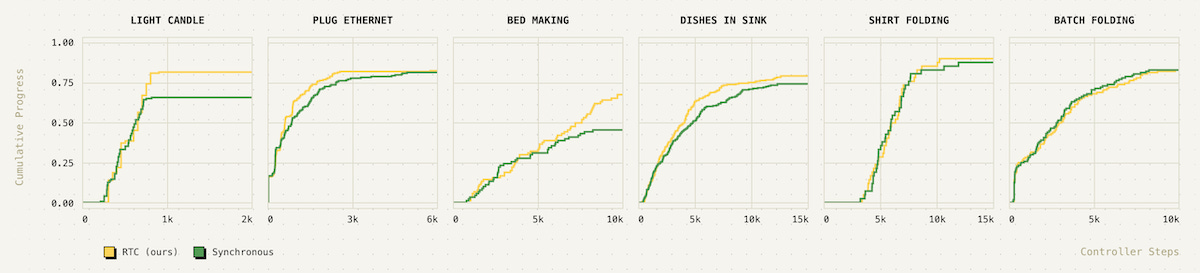
🤖🧠 Real-Time Action Chunking with Large Models
Unlike chatbots or image generators, robots must operate in real time. While a robot is “thinking”, the world around it evolves according to physical laws, so delays between inputs and outputs have a tangible impact on performance. For a language model, the difference between fast and slow generation is a satisfied or annoyed user; for a vision-language-action model (VLA), it could be the difference between a robot handing you a hot coffee or spilling it in your lap. While VLAs have achieved promising results in open-world generalization, they can be slow to run. Like their cousins in language and vision, these models have billions of parameters and require heavy-duty GPUs. On edge devices like mobile robots, that adds even more latency for network communication between a centralized inference server and the robot.
To solve these problems, we developed an algorithm that we call real-time chunking (RTC). It enables real-time execution without discontinuities, and it works on any diffusion- or flow-based VLA — including π0.5 — with no training-time changes. We found that RTC significantly sped up execution time for all the tasks we tested. It was also very robust to latency, even when we injected artificial delays to cause much higher latencies than normal. RTC completed dynamic and precise tasks, like striking a match or plugging in an Ethernet cable, with inference delays of more than 300 milliseconds.
Read more at Physical Intelligence and arXiv
Post-Training Isaac GR00T N1.5 for LeRobot SO-101 Arm using teleoperation data /HuggingFace/ while NVIDIA Isaac Sim™ is now an open-source application on NVIDIA Omniverse for developing, simulating, and testing AI-driven robots in realistic virtual environments /GitHub/
Video Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture 2 (V-JEPA 2) is the first world model trained on video that achieves state-of-the-art visual understanding and prediction, enabling zero-shot robot control in new environments. /Meta/
SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics /arXiv/
Scaling Helix: a New State of the Art in Humanoid Logistics /Figure/
Wandercraft brings in $75M for global acceleration of AI-powered robotics /Tech EU/
Sunrise Robotics, a startup building modular industrial robotics and AI models that makes them simple to deploy in different environments, has emerged from stealth with $8.5 million in seed funding. /Fortune/
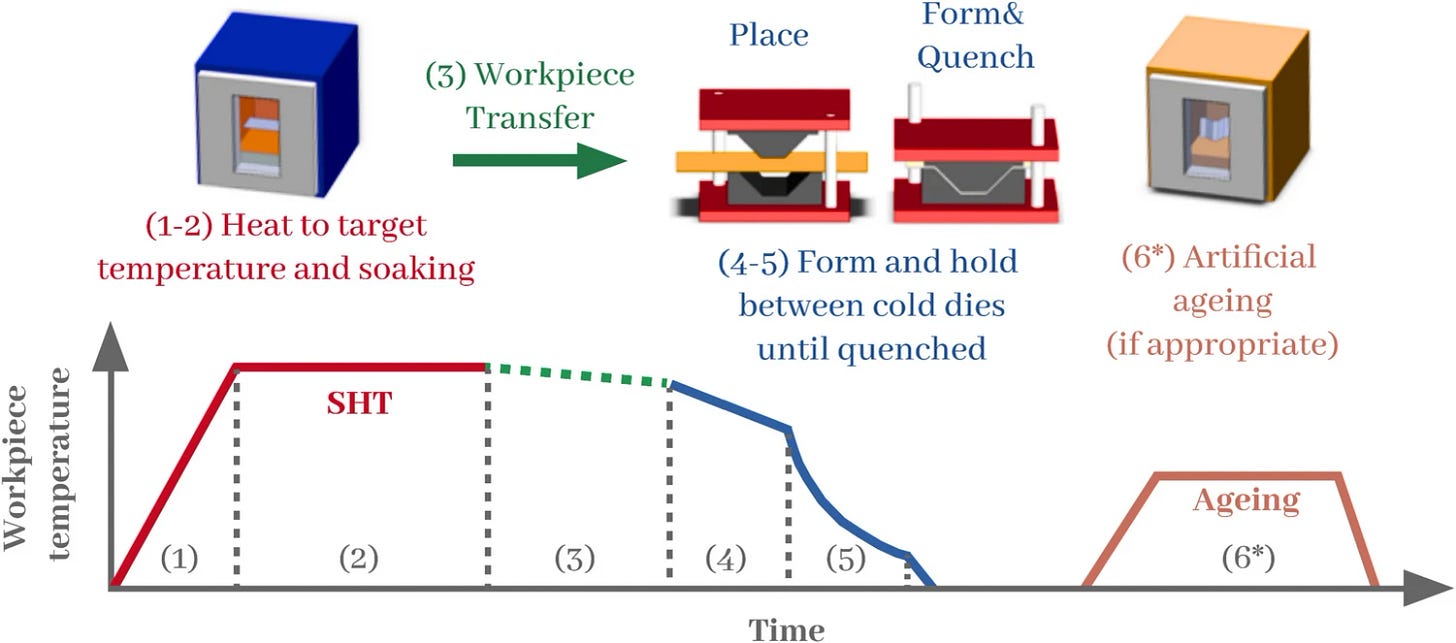
⚙️ Developing thermo-mechanical filters (TMFs) for recognizing information absent hot stamping data
✍️ Authors: Heli Liu, Xiaochuan Liu, Denis J. Politis, et. al
Manufacturing sector is estimated to generate approximately 2000 PB of metadata annually in the near term from both industry and academic activities. Despite this vast data production, a persistent challenge remains in digital manufacturing is that most of the collected manufacturing data are ‘information absent’, primarily due to limitations on data collection methods and data privacy concerns. The information absent data typically lacks one or two critical pieces of information, such as geometric or dimensional features of manufactured products, either for a single data point or specific datasets. The absence of such essential information further deteriorates the long-standing challenge on the significant shortage of labelled manufacturing data. To process the information absent data, the evolutionary binary (EB) algorithm was proposed following thermo-mechanical principles. In a case study, this algorithm enabled the recognition of essential geometric features from an information absent dataset of hot stamping process by labelling the origins of each data point. Serving as a highly flexible framework, the EB algorithm enables the incorporation of a variety of thermo-mechanical filters (TMFs) developed based on data analysis. Results demonstrate that, with the integration of TMFs, the EB algorithm achieved an overall accuracy of nearly 95% with an average computational speed approximately 100 times faster than that of classic machine learning algorithms, despite using extremely sparse labelled data.
Read more at The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology
Understanding Process Damping in Milling Operations /MMS/
New Product Introduction
Highlighting new and innovative facilities, processes, products, and services
🧠📟 Introducing Tulip MCP Server: Bridging Generative AI and Operations
Tulip’s MCP server is our official implementation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for the Tulip platform. The MCP acts as a secure, real-time bridge between large language models (LLMs) and your Tulip instance. This allows AI to read data from and take actions in Tulip through the governed Tulip API. The MCP server makes a variety of Tulip functionalities, such as stations, machines, users, and tables, available as "tools" that an AI agent can use.
Read more at Tulip
Manufacturing Execution Systems: Still Core, Now Smarter /LNS Research/
MES Data Acquisition: How to Unlock Your Factory’s Hidden Data /FlowFuse/
Unlocking Industrial IoT with Litmus MCP Server /Litmus/
Model context protocol (MCP) on Databricks /Databricks/
Siemens and IBM collaborate to bring SysML v2 model-based systems engineering to Siemens Xcelerator
Representing the next milestone in Siemens’ collaboration with IBM to deliver best-in-class model-based systems engineering (MBSE) software, Systems Modeler for SysML v2 is powered by IBM Rhapsody® Systems Engineering. The new software, part of the Siemens Xcelerator portfolio, fully supports the SysML v2 open standard and leverages the two organizations’ decades of systems engineering expertise. SysML v2 is a new modeling language for the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of complex systems and systems-of-systems.
Read more at Siemens
Model-Based Systems Engineering in Electronics /Semiconductor Engineering/

Business Transactions
This week's top funding events, acquisitions, and partnerships across industrial value chains.
Fujitsu launches second corporate venture capital fund to drive innovation and achieve a sustainable society /Fujitsu/
🇺🇸 Gecko Reaches Unicorn Status as Customer Demand Surges Around its Build and Modernization Capabilities
Gecko Robotics, the AI and robotics company developing the platform for building, operating and modernizing the world’s most critical infrastructure, doubled its valuation from its previous funding round, with a Series D valuation of $1.25 Billion. The round was led by new investors Cox Enterprises, and continuing investors USIT, XN, Founders Fund, and YCombinator.
The additional funding will accelerate Gecko's growth and its focus on building and modernizing critical sectors including defense, energy, and manufacturing, which are becoming investment priorities for governments and companies around the world. It comes in the wake of recent announcements such as Gecko’s partnership with NAES to modernize the energy sector, creating a new Extended Reality product with L3Harris, and its growing work with the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company.
Read more at Gecko Robotics and CNBC
Engineer nabs prestigious grants to design insect-inspired, shapeshifting robots /CU Boulder Today/
Delivering a maintenance-free industrial IoT with energy harvesting /New Electronics/
🇨🇦 Waabi Raises $200M USD to Launch Fully Driverless Trucks in 2025
Waabi, a company pioneering generative AI for the physical world, announced it has raised $200 million (USD) in an oversubscribed Series B round, led by Uber and Khosla Ventures. The funding round includes participation from best-in-class strategic investors NVIDIA, Volvo Group Venture Capital, Porsche Automobil Holding SE, Scania Invest and Ingka Investments. Additional financial investors include HarbourVest Partners, G2 Venture Partners, BDC Capital’s Thrive Venture Fund, Export Development Canada, Radical Ventures, Incharge Capital, and others. The new funding, which brings total investment in Waabi to more than $280 million (USD), will support the company’s deployment of fully driverless, generative AI-powered autonomous trucks in 2025.
Read more at Waabi
MAN TruckScenes Dataset /Industrial AI Podcast/ - The World's First Public Dataset For Autonomous Trucking /MAN/
🇺🇸 AIM Automates Construction and Mining with World’s First AI Platform for Heavy Machinery, Announces $50 Million in Funding
AIM, the world’s first embodied AI platform for earthmoving machinery, announced it has raised $50 million to transform the global construction and mining industries. AIM’s investors include Khosla Ventures, General Catalyst, Human Capital, Ironspring Ventures, Mantis, and DCVC, among other great allies. By retrofitting existing heavy equipment with cutting-edge autonomy, AIM enables its customers to achieve maximum safety and productivity. Sites running AIM AI realize massive improvements of their top and bottom lines.
Read more at Business Wire
Bolo AI is Building the Operating System for Heavy Industries With an $8.1 Million Seed Round /Business Wire/
🇬🇧 Q5D secures $13.5 million in funding for wiring automation, including Series A venture round led by Lockheed Martin
Q5D has raised 13.5 million USD in funding to advance its robotic cells that automate product electrification, bringing its total funding to 16.7 million USD. This new funding includes a 2.6 million USD grant (2.0 million GBP) from Innovate UK and a 10.9 million USD Series A co-led by existing investors, Lockheed Martin Ventures, Chrysalix and Maven SWIF, with other investment from SOSV, UKI2S, UntroD and CPI Enterprises.
Q5D’s 5-axis manufacturing robots produce parts on demand and automate embedding wiring directly into the structure of a product, boosting productivity. This process can be co-located with final assembly to simplify supply chains and make them more resilient at a time of turbulence in global trade.
In addition to reducing the cost of logistics, localised wiring automation removes the need for wiring harness inventory and unlocks substantial improvements in wiring efficiency, weight, and reliability. In the automotive sector, conservative estimates suggest Q5D’s technology could cut wiring costs by up to $200 per compact vehicle, while enabling greater supply chain resilience.
Read more at Q5D
RIIICO's AI-based software platform that enables industrial companies to digitally model, redesign, and quickly adapt their established factories (brownfields) to new products or processes raises $5M in Seed funding /Tech EU/
Want more? Check out the paid analysis delivered weekly below 👇