INTEGR8 Spatial Computing & Generative AI
Automation Alley's Integr8 2023 conference showcased how spatial computing and generative AI enable manufacturers to apply expertise at scale.
In the fast-paced world of technology, regional and national non-profit organizations play a vital role in showcasing and promoting innovations. While major industry conferences and exhibitions like HANNOVER MESSE and AUTOMATE attract significant attention, the smaller trade shows organized by non-profit organizations offer a unique platform for participants to dive deeper into vendor solutions and explore emerging companies. These intimate events provide an invaluable opportunity for both established players and companies just starting off to connect with industry leaders, exchange ideas, and showcase their latest technological advancements. INTEGR8 2023 hosted by Automation Alley was no exception.
Automation Alley's Integr8 conference creates a space for collaboration, exploration, and discovery as we tackle the social, economic, and environmental challenges associated with Industry 4.0 and lay the foundations for the innovations of tomorrow.
It wasn’t until a few weeks after the conference when reading Ben Thompson’s piece on Apple Vision Pro did an interesting perspective on INTEGR8 emerge. Specifically, the insight that spatial computing and generative AI are already included in applications empowering human work and productivity across manufacturing, but usability gaps remain before widespread adoption as computing platforms.

Spatial Computing
COVID-19 foisted the spatial computing era onto manufacturers. Being resourceful, manufacturers grabbed the best AR headsets they could find and started to flap their arms and madly gesticulate to direct staff on factory floors across the globe. As OnLogic explains, “Spatial technology isn’t brand new, but it’s getting a renewed moment in the sun thanks to Apple’s latest device.”
Spatial computing uses cameras and sensors to create a digital model or digital twin of people, objects, machines, and their environments, enabling users to interact with them. Interaction and control in spatial computing often uses gestures, body movements, and/or voice commands. Spatial computing combines and builds upon, elements of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and digital twin technologies.
Augmented reality headsets prior to the Apple Vision Pro have come with usability flaws, notably motion sickness and nausea over prolonged use. Early demos of the Apple Vision Pro seem to indicate that Apple has addressed that concern, but it may be too early to tell. If so, it has the potential as a new computing platform for companies to build tailored applications for industrial settings.
The Companies Pursuing Spatial Solutions
The companies at INTEGR8 showcased spatial applications seeking to improve the experience on pre-existing computing platforms (laptop, mobile, cloud). Not one is building on top of Google Glass (RIP), Microsoft HoloLens, or Meta Quest Pro. Maybe that changes next year with the introduction of the Apple Vision Pro.
I’ve listed the companies on display in order of maturity below.
NavVis - Capture and collaborate on the built environment as photorealistic digital twins
Venture Stage: Series D+
Don’t just capture reality—create a new one. In this new reality, you are smarter, more productive, more streamlined, and more creative — because you have the digital foundation to build the world you want to live in. Physical or digital, there is only one reality. And it’s the one NavVis empowers you to build, better.

Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) & mobile mapping - Mobile mapping systems use a combination of highly calibrated sensors and SLAM technology optimized for mapping. These tools enable you to capture 3D point clouds and panoramic images as you walk. They offer fast, comprehensive documentation for large assets and complex environments like factories work sites, and offices.
Scan-to-BIM - The term scan-to-BIM refers to a workflow that uses 3D scanning to document an existing asset and turn it into a BIM model. It was developed as a way to bring existing buildings in line with the latest documentation and planning methodologies.
Digital factories - NavVis IVION Enterprise enables global operations managers to virtually inspect and compare their different production sites all over the world, all from within a web browser.
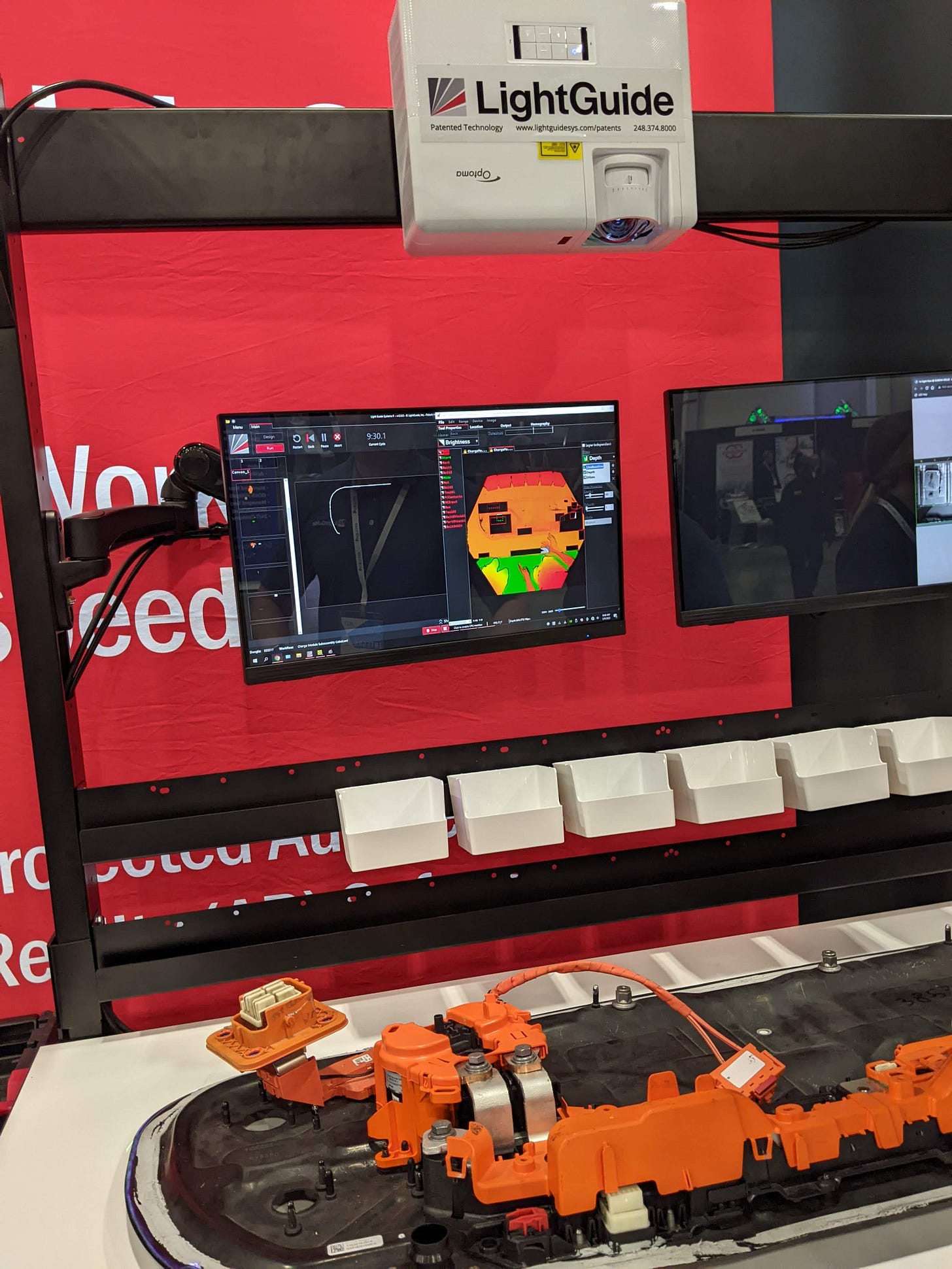
LightGuide - Projected augmented reality work instructions
Venture Stage: Series B
LightGuide’s projected augmented reality (AR) software platform dramatically standardizes and improves any manual process by projecting digital step-by-step work instructions onto an employee’s work surface. From small form factor training to a complex, multi-station work cell assembly, there is a LightGuide projected AR solution for virtually any application.
LightGuide’s current product offerings include:
smartAR™ Workstation: power your core operational processes, from part picking to assembly to testing, inspection, and training. We connect to and communicate with any MES, PLC, or SCADA environment, ensuring the data flows seamlessly across the factory network with no latency.
smartAR™ Desktop: Designed with small form factor parts and processes in mind, it’s ideal for assembly, inspection, repair, and training tasks. This compact platform comes preconfigured with everything your workforce needs to deliver high-quality products every time.
Invisible AI - Automate manual work tracking using intelligent cameras
Venture Stage: Series A
Invisible AI’s platform enables manufacturers without any coding or engineering expertise through:
Assembly Monitoring - Continuously improve operation productivity & safety with data analytics on standardized work and walk-wait times tracking.
Digital poka yoke - Accelerate mistake-proof operations with the detection of common simple mistakes in real-time.
Smart Search - Facilitate quality check by finding the operations associated with part ID or any given timeframe.
Motion Tracker - Provide clear visibility on all manual work operations by tracking individual body joints.
Ergonomics Monitor - Assist monitoring of safety measures by tracking human behavior and ergonomics in real-time.
Khenda - AI-powered video analytics and digitized engineering tools
Venture Stage: Seed
Khenda is designed to help the manufacturing industry overcome common challenges and achieve operational excellence. Their platform streamlines the DMAIC process, reduces waste, and boosts efficiency through AI-driven video analytics and digital engineering tools that bridge the gap between manual operations and digitization.
Khenda offers an array of software modules, including:
Measure: Automate cycle time measurements with AI-driven video analytics.
Work Instructions: Develop clear, standardized operating procedures.
Digital Time Study: Identify value-adding and non-value-adding processes.
MTM: Perform Methods-Time Measurement (MTM) analysis with digital tools.
Line-balancing: Optimize workload distribution across workstations.
Lean Assistant: Utilize AI to automate the creation of FMEA tables, hazard analysis, and more.
CrossBraining - Remote training that works
Venture Stage: Seed
Their training platform revolutionizes how you train your staff and customers by having them teach back the skills they are supposed to know (Proof of Skills). Giving you a way to do hands-on training anywhere, anytime. No more scheduling hassle and travel costs. With CrossBraining, you train hands-on skills as if you were standing right there.
Generative AI
Microsoft MVP of AI Charles Elwood hosted a roundtable on artificial intelligence with the top takeaway being the rapid pace of change enables manufacturers to shortcut communication tasks. This is also validated by a recent McKinsey report where decision-making and collaboration have the biggest automation potential due to the development of Generative AI. But, whether it’s an AI chatbot or an industrial engineer delivering a status report it must be timely and accurate. Current generative AI models have nasty hallucinations that hinder usability and can lead to bad outcomes in industrial settings.

The Companies Pursuing Generative AI
There was only one company, Andonix, showcasing their AI-powered manufacturing assistant, named Andi.
Andonix - Connected Worker Solutions for the frontline workforce
Venture Stage: Seed
Andonix connects your team to their management, work, training, and to each other through user-friendly mobile technology.
Andonix recently introduced Andi, the AI-powered manufacturing chatbot designed to bring AI augmentation to factory workers. Andi is an advanced natural language processing solution driven by AI technology, enabling factory workers to engage in human-like conversations and request expert help and support from the chatbot. Andi can assist with tasks such as automatically monitoring machine and process performance, solving problems, and generating action plans, checklists, and work instructions. The company claimed Andi supports OpenAI’s newest model, GPT-4.
INTEGR8 Industry 5.0
Both Generative AI and Spatial Computing have to potential to kickstart Industry 5.0. As Clarify puts it,
The concept of Industry 5.0 is mostly focused on the integration of humans working alongside robots and IoT devices in the automated industrial environments of the future. As opposed to Industry 4.0 which was mostly about leveraging robots and smart machines for maximum efficiency and high performance in manufacturing, Industry 5.0 is centered around the human impact and how the latest technologies, such as IoT and Big Data, can be leveraged to empower human work and capabilities.
These two technologies are centered around humans rather than robots. The solutions at INTEGR8 showed how humans can collaborate better, improve safety, and increase labor productivity. We shall see how spatial and generative AI applications evolve to be harnessed by humans in factories across the globe.